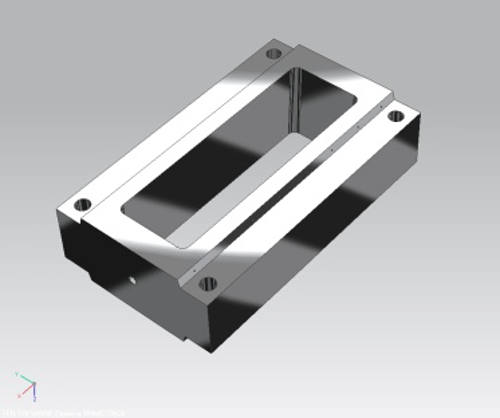
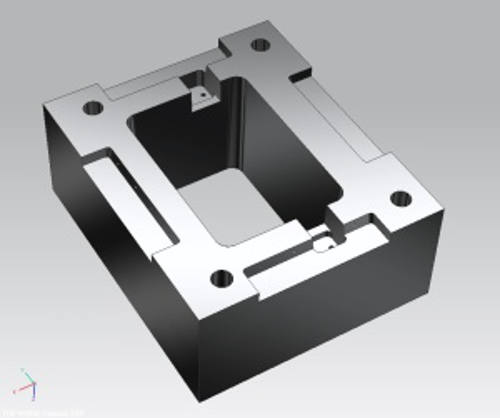
Cutting sectors of press brake blades
For example, the blades of press brakes, or the blades of planes for wood.
Cutting to size pieces of workpieces that have already been tempered or even hardened in some places is a considerable cost.
Cutting with abrasive disks is not precise, and the cutting area is tempered. It is therefore necessary to leave a certain amount of metal, with the duplicate purpose of measuring by grinding, and remove the part found.
The cut is fast, the grinding a little less, but almost always the two phases are carried out manually, and require qualified personnel, despite their simplicity.

Wire erosion is often used, which has the advantage of not letting the material come to light, and of obtaining a precise and geometrically accurate cut. The hourly cost of operation, (wire, demineralized water, ion exchange resins, filters, etc..), greatly limit the use. Only in case the machine is out of work, closing the eyes on costs, is it used for this purpose.
E.cut represents a revolutionary solution! In addition to the characteristics of a wire erosion machine, it has some notable advantages.
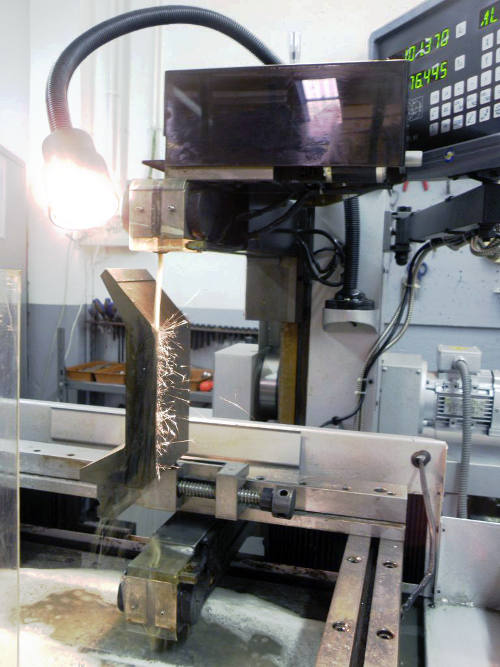

-Do not work by immersion, so the pieces can escape from the pallet.
-The maximum thickness of cut is 300mm already from the smallest models, allowing to overlap more blades.
-The hourly cost of operation does not exceed 0.4 €/hour, compared to 4 €/hour of the cheaper conventional wire erosion.
-Management and maintenance are extremely simple, and do not require specific skills.
-The purchase cost of an Ecut is 4 to 8 times lower than conventional wire erosion.
Machines that can cut up to 800 mm in height are possible.